Spina-bifida surgery in Hyderabad | Dr Vishakha
Spina bifida ( literally means -split spine) – more appropriately called as Spinal dysraphism is a congenital condition involving abnormal formation of structures in the spine, including the bone, the spinal cord, and the nerve roots during first month of pregnancy.
So it occurs , often before a mother comes to know that she is pregnant. As spine develops from neural tube , this is referred as neural tube defect (NTD). It occurs in 1in 1000 live births.
How to identify spinal dysraphism ?
– presence of hairy patch, dimple, dark spot on the back since birth
– presence of swelling on the infant’s back in the midline since birth
– presence of dimple or sinus (small hole) on the back
So every child born should undergo thorough evaluation of the spine by a clinician to rule out presence of any neural tube defect.
What are the types of spinal dysraphism ?
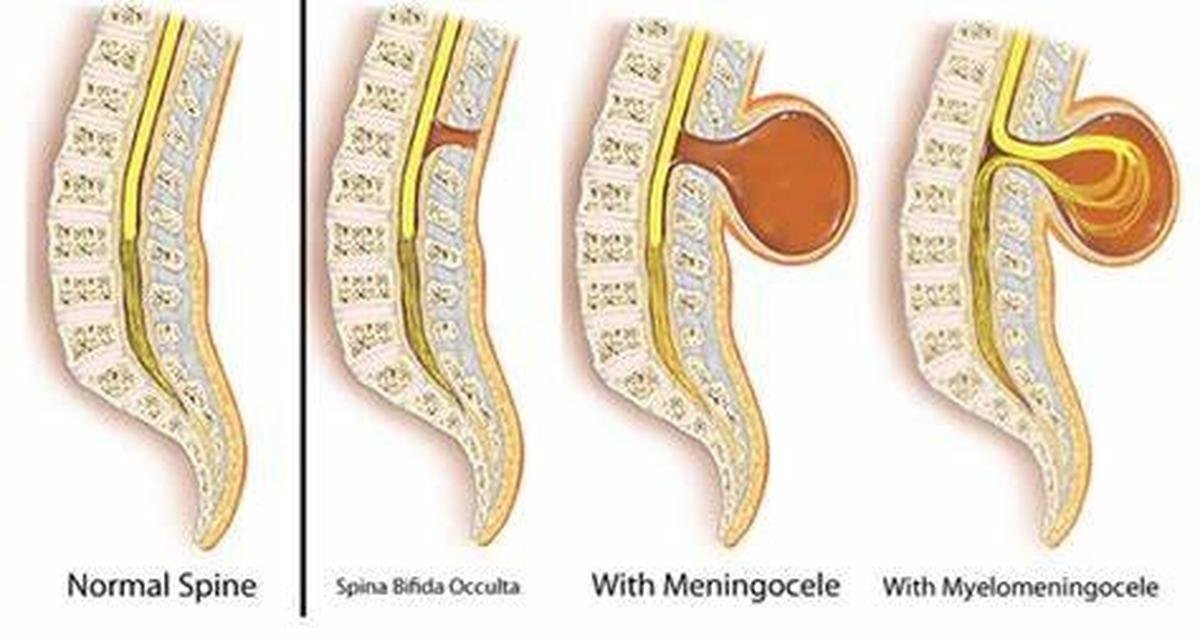
- Spina bifida :. This is mildest and most common form of the spinal dysraphism occuring in 10-20% of children. In this form, one or more of the bones in the spine (vertebrae) don’t unite properly. Most of the times it is associated with open or closed neural tube defect.
- Closed neural tube defect – In these type of defects, neural structures are not exposed , they are either covered by sac or skin. But there can be various malformations present in fat, spine bone, membranes on the spinal cord, spinal cord & nerves.
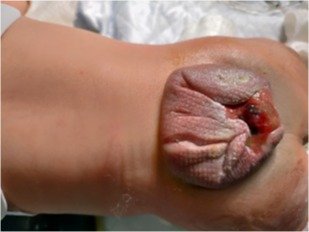
- Open neural tube defect. – In such cases, neural structures are exposed with CSF (cerebrospinal fluid)leak, they are not covered by either sac or skin. (eg. Ruptured meningocele & myelomeningocele). These babies might have less favourable prognosis than closed neural tube defects.
Types of neural tube defects:
- Meningocele. – Membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord protrude through an opening in the spinal column and form swelling in the back.
- Myelomeningocele. -This is the most severe form of spina bifida. It occurs when the spine bones fail to close and the spinal cord along with nerves protrude through the defect in the spinal column forming swelling in the back. Children with this type are often fully or partially paralyzed, have difficulty with bladder and bowel control, have orthopedic problems, and may have problems of drainage of cerebrospinal fluid causing hydrocephalus.
- Tethered cord – Spinal cord is tightly held by a band like structure called as filum terminale.
- Spinal lipoma – Abnormal fat tissue attached to spinal cord
- Diastematomyelia – Spinal cord id divided in to two halves.
What are the symptoms of spinal dysraphism?
The symptoms vary widely depending on the type of spinal dysraphism a child has.
Many children may not have any symptoms or might have only have mild symptoms. These may include:
-a small clump of hair or a dimple or birthmark on the spine
-chronic constipation with no other cause
-chronic urinary or bowel incontinence with no other cause
-chronic urinary tract infections
-Recurring leg or back pain
-Limping, Toe walking
-scoliosis/ curved spine
Few children have symptoms that are noticeable at birth, such as an small opening in the spine or swelling with a sac that protrudes from the spine.
What are the associated medical conditions found with neural tube defects ?
The associations and complications of spinal dysraphism vary according to the type and its severity of malformation.
Associated conditions can include:
– Hydrocephalus ( increased water in brain)
– Chiari malformation (type II) – herniation of hindbrain
– Spine curvature deformities – scoliosis, kyphosis,
– Neurological issues such as weakness in the legs or feet, back pain or leg pain
– Orthopedic (bone) problems, such as hip dislocation, joint deformities, and clubfoot
– Urological issues – bladder or bowel disturbances, urinary tract infections or kidney damage
– Impaired cognitive development and learning disabilities, seizures.
What are the causes of spinal dysraphism ? Can it be prevented?
The exact cause of spinal dysraphism unknown. Causative factors may be genetic, nutritional, and environmental. Many research studies have proved that deficiency of folic acid (a component of vitamin B ) in a pregnant woman has more risk of developing spinal dysraphism in baby. Hence, a daily folic acid supplementation is recommended for all women of child-bearing age, or atleast 3 months prior to pregnancy.
Does spinal dysraphism condition runs in family ?
In more than 90 percent of cases, none of the family members have got spinal dysraphism. However, if one parent has spinal dysraphism, there’s a one in 25 (4 percent) chance of passing it to your baby. If already one child is born with spinal dysraphism, there’s a one in 25 (4 percent) chance that second child might be having spinal dysraphism. So, If your previous child or family member has a neural tube defect, please consult your doctor before planning pregnancy and start a daily folic acid supplementation before planning pregnancy.
There is increased risk up to 10-fold (than normal mothers) if pregnant mother has diabetes.
If mother is on certain anti-seizure medications (e.g., valproic acid and carbamazepine), which inhibit folate metabolism, increases the relative risk of neural tube defect in baby. So , please consult your doctor before planning pregnancy ,if you are on these medications
Can neural tube defects be diagnosed during pregnancy?
Yes. They can usually be detected in the fetus, but not always. These tests include:
Routine ultrasound (USG): Few defects in the fetus’s spine can be detected through imaging.
Serum AFP: This screening blood test tests the AFP (alpha-fetoprotein) level in the blood during the 16th to 18th week of pregnancy,. The AFP levels is higher in about 75% to 80% in women who carry a fetus with neural tube defects.
Fetal MRI – Detects the fetal spinal malformations in more detail than USG.
How to treat spinal dysraphisms / neural tube defects?
Thorough physical examination, urological assessment and urodynamic testing, and radiological evaluation with MRI of spine should be done.
Once the type of neural tube defect and its severity is determined, the timing and type of surgery is decided for repair of those defects.
Other Possible treatments a child may need include:
– Surgery for CSF (cerebrospinal fluid) diversion – Endoscopic (ETV) or shunting for hydrocephalus
– Bladder augmentation , reconstructive bladder surgery
for neurogenic bladder/ urinary disturbances
– Bowel surgery for bowel incontinence
– Bracing or orthopedic surgery for associated foot deformities
– Spine surgery for scoliosis
– Physical therapy (PT) or occupational therapy (OT)
– An Individualized Education Program (IEP) for cognitive problems
How we care for spinal dysraphisms at Rainbow children’s Hospital?
Antenatal diagnosis (diagnosis before birth)-
Our expert obstetricians and fetal medicine specialists uses biomarkers and best radiological imaging techniques to diagnose neural tube defects at the earliest, so that a proper action plan of treatment can be formulated after birth of a child. Proper maternal counselling is given by expert obstretitians and fetal medicine experts.
Postnatally diagnosed (diagnosed after birth)-
Our dedicated and expert team of specialists works together and develop a comprehensive, personalized and coordinated care plan for treatment of child with spinal dysraphism. As we know that these children might need lifelong follow up, our special team of (Spinal dysraphism care team) doctors provide age-appropriate care at each developmental stage, to reduce the disabilities if any and prepare the child to live more productive and independent life.
We are one of few centers in India and the world that offers comprehensive, coordinated care plan including all necessary specialties needed for treatment of children having spinal dysraphism under one roof.
Our dedicated Spinal dysraphism care team includes –
- Pediatric neurosurgeon
- Pediatric neurologist
- Fetal medicine experts
- Neonatalogist and intensivist
- Pediatric surgeon and urologist
- Pediatric Orthopedic surgeon
- Radiologist
- Physiotherapist and ocuptional therapist
- Genecist
- Nutritionist
Dedicated nurse practitioner and team coordinator
What are the recent technologies in the treatment of these spinal dysraphisms?
Our team of expert neurosurgeons, perform surgery using high end microscope and Intraoperative neuromonitoring (IONM) to increase the safety of surgery and reduce the risk of neurological deficits & disabilities after surgery.
Proficiency of Dr Vishaka:
- Hydrocephalus (increased fluid in the brain) Treatment:
Endoscopic third ventriculostomy and CSF diversion (VP shunt) , neuroendoscopic
procedures for complex hydrocephalus. - Craniosynostosis (abnormal head shape due to untimely cranial sutures fusion) :
- Treatment –
Helmet therapy , endoscopic and open surgery. - Spinal dysraphisms(Spina Bifida)-
(spinal abnormalities present since birth) – surgical repair - Encephalocele repair surgery.
- Vascular and stroke surgeries:
revascularization surgeries for moya moya disease, emergency surgery for stroke - Pediatric brain and spine tumour surgeries.
- Pediatric brain and spine infection surgeries:
Endoscopic and open surgeries for brain and spine infections. - Pediatric traumatic brain and spinal injury.
- Antenatal counselling for congenital fatal neurosurgical conditions.
Dr Vishakha Karpe M.B.B.S, DNB (AIIMS) New Delhi, M.Ch (IPGMER SSKM) Member of “The Royal College of Surgeons, Edinburgh” (U.K.) is a highly competent and one of the best pediatric neurosurgeons in Hyderabad, Telangana with 13 years of experience, is among the topmost pediatric neurosurgeons in the Rainbow group of hospitals at Banjara Hills and Hyder Nagar.