What is a brachial plexus?
The brachial plexus is a vital nerve network in the human body. It originates from the spinal cord in the neck and extends through the shoulder to control movement and sensation in the arm, forearm, and hand. It comprises the ventral rami (nerve roots) of C5, C6, C7, C8, and T1, with some contributions from C4 and T2 in specific individuals. This intricate network is crucial in human physiology, ensuring proper functioning and sensory perception.
What are the types of brachial plexus injuries in children?
- Brachial Plexus Neuritis is a rare inflammatory disorder affecting children, often resulting from viral infections, vaccinations, or immune responses. It causes sudden shoulder pain and arm muscle weakness, typically improving with physical therapy, but some may still experience residual weakness.
- Congenital brachial plexus malformations, caused by genetic or intrauterine issues, can cause weakness, lack of movement, or sensory deficits in affected limbs. Diagnosis often requires MRI or nerve conduction studies; treatment may include therapy or surgery.
- Falls, sports injuries, or accidents primarily cause childhood brachial plexus injuries. These injuries can result in partial or complete nerve tears or avulsion, causing weakness, pain, or full loss of function in the affected limb. Treatment options include physical therapy for mild cases and nerve grafts or transfers for severe cases.
- Neurofibromas, schwannomas, or other tumours can compress the brachial plexus in children, causing chronic pain, weakness, or sensory changes. Diagnosis requires imaging like MRI, and treatment may involve surgical removal if symptoms are significant.
- Radiation-induced brachial plexopathy is a rare condition in children undergoing radiation therapy for cancers near the brachial plexus, causing progressive weakness and sensory loss in the arm, requiring symptom management and treatment.
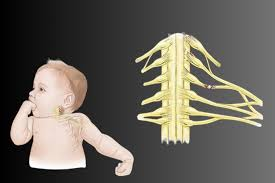
What are the symptoms and causes of brachial plexus?
Symptoms
Brachial Plexus injuries in children can cause weakness, numbness, pain, decreased range of motion, and muscle atrophy. Symptoms include weakness or paralysis of the arm, shoulder, or hand, tingling sensations, discomfort, reduced range of motion, and muscle atrophy in the affected arm or hand. It is crucial to seek medical attention if these symptoms persist.
Causes
Brachial plexus injuries in children can be caused by birth trauma, motor vehicle accidents, falls from heights, contact sports like football or hockey, and non-accidental trauma like child abuse. Birth trauma can result from a stretched or pulled shoulder during delivery, while car accidents can result from ejection from the vehicle or a car strike. Falls from trees or playground equipment can also cause brachial plexus injuries.
What are the surgical guidelines for treating children with brachial plexus injuries?
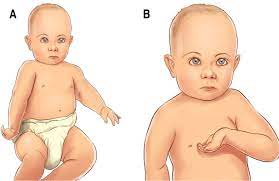
Pre-surgical guidelines
The process involves obtaining imaging studies like MRI or CT scans to assess the injury’s extent and plan the surgical approach. Electromyography and nerve conduction studies evaluate muscle function and identify nerve damage areas. A comprehensive surgical plan outlines the strategy, incision, and repair technique. Additionally, parental education is provided.
Surgical guidelines
The surgical approach involves meticulous surgery to minimize tissue damage and preserve nerve function. Nerve repair is performed using microsurgical techniques and sutures or grafts as needed. Nerve transfer and muscle transfer procedures are also considered to restore function in affected muscles.
Intraoperative guidelines
Intraoperative nerve monitoring assesses nerve function and guides surgical decision-making. Intraoperative imaging, like ultrasound or fluoroscopy, aids in decision-making. Hemostasis is achieved meticulously to minimize bleeding and reduce complications.
Post-operative guidelines
Pain management, wound care, rehabilitation, and follow-up care are critical to a patient’s recovery. It also includes devising a comprehensive strategy to reduce suffering and increase healing, providing precise wound care to reduce infection risk, launching a rehabilitation program, and scheduling regular appointments to monitor progress and adjust treatment plans.
Pediatric-specific considerations
When planning surgical treatment, consider the child’s age and developmental stage, the size and delicacy of nerves in children, and the potential impact of surgical treatment on growth and development. Provide family-centered care, involving parents and caregivers in the treatment plan and decision-making process.
Multidisciplinary team
A pediatric neurosurgeon, orthopaedic surgeon, pediatric anesthesiologist, physical therapist, and occupational therapist are essential professionals in pediatric surgery, including brachial plexus surgery, musculoskeletal surgery, pediatric anaesthesia, physical rehabilitation, and occupational rehabilitation. Following these guidelines ensures optimal care and outcomes for children undergoing surgical treatment for brachial plexus injuries.
The brachial plexus is a vital nerve network responsible for the upper limb’s movement and sensation. Its anatomy and function are crucial for diagnosing and managing neurological and musculoskeletal conditions. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve outcomes and restore limb functionality. Advancements in nerve repair techniques are improving medical interventions for brachial plexus injuries. Early diagnosis and intervention are vital for children who can regain significant function with proper therapy and surgery.
About Dr Vishakha :
Dr Vishakha Basavraj Karpe is a highly skilled senior consultant at Rainbow Children’s Hospital in Banjara Hills and Hydernagar Hyderabad. She is known for her comprehensive care approach and is one of the few dedicated leading paediatric neurosurgeons in the city and India with over ten years of extensive experience in pediatric neurosurgery. Her expertise includes treating hydrocephalus, spinal dysraphism, craniosynostosis, paediatric brain infections, brain and spine tumours and stroke surgery.
She has a special interest in craniosynostosis surgery, which is done only in very few centres in India.
Proficiency of Dr Vishakha:
-
- Hydrocephalus (increased fluid in the brain): The procedure involves an endoscopic third ventriculostomy and CSF diversion (VP shunt) to treat complex hydrocephalus.
- Craniosynostosis (abnormal head shape due to untimely cranial sutures fusion) surgeries: Helmet therapy is a technique that is used in both endoscopic and open surgery.
- Spinal dysraphisms(Spina Bifida)- (spinal abnormalities present by birth) – surgical repair
- Encepahaocles repair surgery.
-
- Vascular conditions and stroke surgeries: revascularization surgeries for moya moya disease.
- Pediatric brain and spine tumour surgeries.
-
- Pediatric brain and spine infection surgeries: Endoscopic and open surgeries for brain and spine infections.
- Pediatric traumatic brain and spinal injury.
- Antenatal counselling for congenital fatal neurosurgical conditions.





