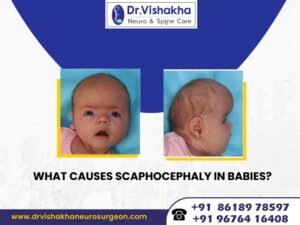
Neck pain in children can range from mild to severe and can be caused by muscle strain or overuse. However, some cases may indicate a more serious underlying condition. This growing concern requires prompt attention from healthcare providers, parents, and caregivers. While many cases can be managed with self-care and over-the-counter pain relievers, some require medical attention. Recognizing when to seek medical attention is crucial, as some symptoms may indicate serious underlying conditions. A comprehensive overview of signs that warrant a doctor’s visit is provided.
Common causes of neck pain
Various factors, including muscle strain, poor posture, herniated disk, arthritis, and injuries, can cause neck pain. A muscle strain occurs when the neck muscles are overused, while poor posture strains the neck muscles and joints. Herniated disks can pressure nerves, while arthritis can cause neck pain and stiffness. In children, serious neck pain can result from trauma, infections, and congenital conditions. Trauma can cause fractures, dislocations, or ligament sprains, while infections like meningitis or septic arthritis can cause neck pain. Congenital conditions like Klippel-Feil syndrome or Down syndrome can increase the risk of neck pain and instability.
Serious symptoms that require medical attention
Neck pain can be managed at home, but certain symptoms require immediate medical attention. These include sudden severe pain, numbness or tingling in the arms or legs, weakness or paralysis, difficulty walking or maintaining balance, loss of bladder or bowel control, fever, swollen lymph nodes in the neck, and difficulty swallowing. If these symptoms persist or worsen, it is crucial to seek medical attention. Children with severe neck pain may experience stiffness, limited mobility, numbness, tingling, weakness in their arms or legs, and struggle with swallowing, breathing, or speaking. Untreated or undertreated serious neck pain in children can lead to long-term complications, including chronic pain, limited mobility, neurological deficits, and psychological distress, such as anxiety and depression. Healthcare providers should provide comprehensive treatment and follow-up care to minimize the risk of complications and promote optimal outcomes.
Treatment and prognosis
Treatment
Pain management involves using over-the-counter pain relievers, physical therapy, and orthopaedic devices to manage inflammation and pain. Physical therapy improves range of motion, strength, and flexibility. Orthotics and assistive devices support the neck and promote healing. Surgery may be necessary for underlying conditions like spinal cord injuries or tumours. Alternative therapies like acupuncture, massage, or chiropractic care can complement traditional treatment.
Prognosis
The prognosis for serious neck pain in children varies based on the cause and severity of symptoms. Mild cases, such as muscle strain or overuse, can recover with rest, physical therapy, and pain management. Moderate cases, like torticollis or juvenile idiopathic arthritis, may require ongoing treatment but still achieve significant improvement. Severe cases, like spinal cord injuries or tumours, may face a more guarded prognosis with potential long-term consequences like chronic pain, limited mobility, or neurological deficits. Chronic pain can lead to complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS), limited mobility can result from untreated or undertreated neck pain, and neurological deficits can result from spinal cord injuries or tumours. Chronic neck pain can also have a significant psychological impact, leading to anxiety, depression, or decreased quality of life.
Follow-up care
Regular follow-up care with a healthcare provider is crucial for monitoring progress, preventing complications, and promoting optimal outcomes in children with serious neck pain. This includes adjusting treatment plans, addressing concerns or complications, identifying potential complications early, and ensuring the child receives the best possible treatment, rehabilitation, and support. By providing comprehensive care, healthcare providers can help children improve their quality of life.
Prevention and Awareness
A proactive approach is needed to prevent severe neck pain in children. This includes education on neck pain risks and symptoms, teaching proper posture, lifting techniques, and safety habits, and healthcare providers being aware of signs and symptoms and providing prompt and effective treatment.
Serious neck pain in children is a growing concern that requires immediate attention from healthcare providers, parents, and caregivers. Understanding this condition’s causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment can improve outcomes, minimize complications, and enhance the quality of life for affected children. A proactive approach to preventing serious neck pain in children is crucial, along with comprehensive treatment and follow-up care. This approach can help prevent complications, improve the overall quality of life, and ensure optimal outcomes for affected children. Therefore, it is essential to take a proactive approach to addressing this growing issue.
About Dr Vishakha :
Dr Vishakha is a highly skilled senior consultant at Rainbow Children’s Hospital in Banjara Hills and Hydernagar Hyderabad. She is known for her comprehensive care approach and is one of the few dedicated leading paediatric neurosurgeons in the city and India with over ten years of extensive experience in pediatric neurosurgery. Her expertise includes treating hydrocephalus, spinal dysraphism, craniosynostosis, paediatric brain infections, brain and spine tumours and stroke surgery. She has a special interest in craniosynostosis surgery, which is done only in very few centres in India.
Proficiency of Dr Vishakha:
-
- Hydrocephalus (increased fluid in the brain): The procedure involves an endoscopic third ventriculostomy and CSF diversion (VP shunt) to treat complex hydrocephalus.
- Craniosynostosis (abnormal head shape due to untimely cranial sutures fusion) surgeries: Helmet therapy is a technique that is used in both endoscopic and open surgery.
- Spinal dysraphisms(Spina Bifida)- (spinal abnormalities present by birth) – surgical repair
- Encepahaocles repair surgery.
-
- Vascular conditions and stroke surgeries: revascularization surgeries for moya moya disease.
- Pediatric brain and spine tumour surgeries.
-
- Pediatric brain and spine infection surgeries: Endoscopic and open surgeries for brain and spine infections.
- Pediatric traumatic brain and spinal injury.
- Antenatal counselling for congenital fatal neurosurgical conditions.