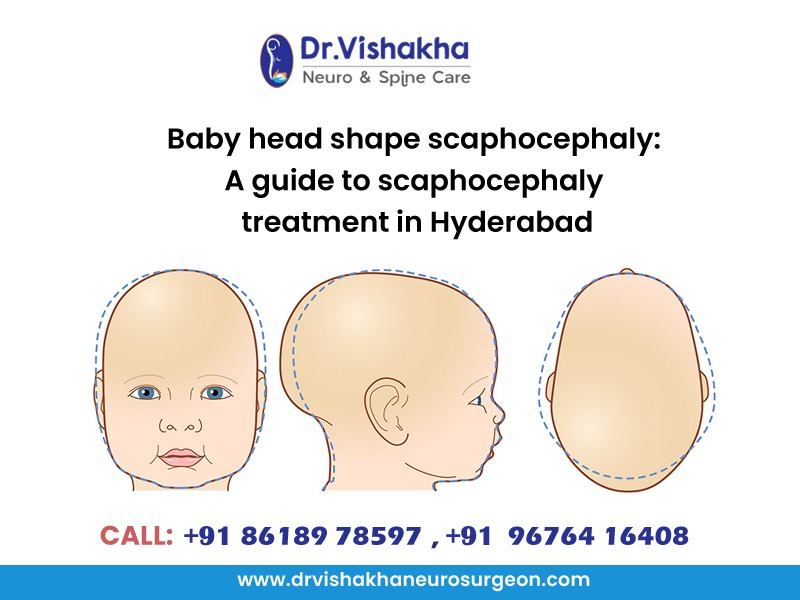
Scaphocephaly, as explained by Dr Vishakha Basavraj Karpe, the best paediatric neurosurgeon, is a type of craniosynostosis characterised by an elongated head shape. This condition occurs when the sagittal suture, which runs from the front to the back of the skull, fuses prematurely. As a result, the skull cannot expand normally, leading to a shape that appears narrow and long rather than rounded.
Key Aspects of Scaphocephaly:
The defining feature of scaphocephaly is the elongated appearance of the head. The forehead may appear prominent, and the back of the head may be flat. This shape can become more noticeable as the child grows.
- Causes: While the exact cause of scaphocephaly is often unknown, it can occur as an isolated condition or as part of a syndrome that affects skull and facial development. Genetic factors may also play a role.
- Diagnosis: Scaphocephaly is typically diagnosed through a physical examination and can be confirmed with imaging studies, such as a CT scan. These imaging techniques help visualize the skull’s sutures and confirm the presence of any fusion.
- Symptoms: Aside from the distinct head shape, most children with scaphocephaly do not exhibit symptoms related to brain development. However, in some cases, if the condition leads to increased intracranial pressure, it could cause headaches, irritability, or developmental delays.
- Treatment: The primary treatment for scaphocephaly is surgical intervention, typically performed in the first year of life. The surgery aims to correct the shape of the skull, relieve pressure on the brain, and promote normal brain growth. Approaches may include a craniectomy or cranial vault reconstruction, depending on the severity.
- Prognosis: With timely surgery and proper follow-up care, children with scaphocephaly can achieve normal head shape and development. Long-term outcomes are generally positive, and many children lead healthy lives.
Overall, early diagnosis and intervention are key to managing scaphocephaly effectively, ensuring that the child’s brain has the opportunity to grow and develop normally.
A guide to scaphocephaly treatment in Hyderabad by Dr Vishakha Basavraj Karpe, the best paediatric neurosurgeon
The treatment for scaphocephaly primarily involves surgical intervention aimed at correcting the abnormal head shape and allowing for normal brain growth. Here’s an overview of the treatment process:
Surgical Intervention
Surgery is typically recommended within the first year of life, often between 3 to 12 months, depending on the child’s specific needs and the severity of the condition. Early intervention is crucial for optimal outcomes.
Types of Surgery:
Cranial vault reconstruction (CVR):
Objectives of Cranial Vault Reconstruction
Correct Head Shape: The primary goal of CVR is to restore a more typical head shape by expanding the skull in the areas that are flattened or narrow.
Allow Brain Growth: By restructuring the skull, the surgery aims to relieve any pressure on the brain and ensure adequate space for normal brain development.
Surgery details
- Preoperative Assessment: Prior to surgery, the child undergoes a comprehensive evaluation, which may include imaging studies (like a CT scan) to assess the skull’s structure and to plan the reconstruction. Consultations with a pediatric neurosurgeon and/or craniofacial surgeon are part of the preparation.
- Anesthesia: The procedure is performed under general anesthesia, ensuring that the child is completely unconscious and pain-free during the operation.
- Incision: The surgeon makes a large incision along the top of the head to access the skull. The specific location and design of the incision may vary based on the surgeon’s technique and the child’s needs.
- Reshaping the Skull:The surgeon removes the conforming part of the skull vault, including pieces of bone that have abnormally fused. The procedure allows the cranial bones to be reshaped into a more normal contour.The removed bone segments may be reshaped and then replaced, or new materials may be used to augment the structure.
- Fixation: Once the skull is reconstructed, the surgeon uses plates, screws, or absorbable materials to secure the bones in their new position. This helps maintain the desired shape as the child grows.
- Closing the Incision: After the reconstruction is complete, the surgeon carefully closes the incision with sutures or staples, ensuring that the scalp is positioned correctly.
Stripping Craniectomy surgery:
Objectives of Stripping Craniectomy
- Release Premature Fusion: The primary goal is to remove the fused section of the sagittal suture, allowing the skull to expand normally.
- Improve Head Shape: By correcting the skull’s shape, the surgery aims to minimize the elongated appearance associated with scaphocephaly.
- Facilitate Normal Brain Growth: Ensuring adequate space for the brain to grow without the constraints of a malformed skull is crucial for healthy development.
Surgery details
- Preoperative Assessment: Before the surgery, the child undergoes a thorough evaluation, including a physical examination and imaging studies (such as a CT scan) to assess the skull and plan the procedure.Consultation with a pediatric neurosurgeon or craniofacial specialist is also standard.
- Anesthesia: The procedure is performed under general anesthesia, ensuring the child is comfortable and pain-free during the surgery.
- Incision: The surgeon makes an incision along the scalp, typically in a way that minimizes scarring. The length and placement of the incision depend on the individual case.
- Suture Removal: During the surgery, the surgeon carefully exposes the fused sagittal suture and removes the fibrous tissue connecting the adjacent skull bones. This releases the constraint on the skull’s growth
- Reshaping the Skull: After releasing the suture, the surgeon may also reshape the skull if necessary. This can involve modifying or repositioning certain bone segments to achieve a more typical head shape.
- Closure: Once the surgery is complete, the incision is closed using sutures or staples. The surgeon ensures that the scalp is properly aligned and secured.
Postoperative Care
- Hospital Stay: Children typically remain in the hospital for a short period (usually 1-3 days) for monitoring, pain management, and observation to ensure there are no complications.
- Pain Management: Pain relief is an important aspect of recovery, and medications will be provided to keep the child comfortable.
- Wound Care: Parents will receive detailed instructions on how to care for the surgical site, including keeping the area clean and monitoring for signs of infection.
- Long-Term Follow-Up: Regular check-ups with the surgeon are essential to monitor the child’s recovery and head shape over time. This may include imaging studies to assess bone growth and ensure that the skull is developing normally.
- Developmental Monitoring: Ongoing assessments of the child’s cognitive and physical development are important, as early intervention can support optimal outcomes.
- Physical Activities: Parents will be advised on when it is safe for their child to resume normal activities and play. Initially, it’s important to avoid any activities that could put pressure on the head.
- Ongoing Support: Therapy and Support Services: Depending on the individual child’s needs, additional therapies, such as occupational or physical therapy, may be recommended to support their development.
- Monitoring Development: Continuous monitoring of the child’s cognitive and physical development is essential. Most children with scaphocephaly who undergo treatment can achieve healthy growth and development.
With early diagnosis and comprehensive treatment, most children with scaphocephaly can achieve positive outcomes, gaining a more typical head shape and normal brain development. The chances of long-term complications are significantly minimized with timely surgical intervention.

About Dr Vishakha :
Dr Vishakha Basavraj Karpe is a highly skilled senior consultant at Rainbow Children’s Hospital in Banjara Hills and Hydernagar Hyderabad. She is known for her comprehensive care approach and is one of the few dedicated leading paediatric neurosurgeons in the city and India with over ten years of extensive experience in pediatric neurosurgery. Her expertise includes treating hydrocephalus, spinal dysraphism, craniosynostosis, paediatric brain infections, brain and spine tumours and stroke surgery.
She has a special interest in craniosynostosis surgery, which is done only in very few centres in India.
Proficiency of Dr Vishakha:
-
- Hydrocephalus (increased fluid in the brain): The procedure involves an endoscopic third ventriculostomy and CSF diversion (VP shunt) to treat complex hydrocephalus.
- Craniosynostosis (abnormal head shape due to untimely cranial sutures fusion) surgeries: Helmet therapy is a technique that is used in both endoscopic and open surgery.
- Spinal dysraphisms(Spina Bifida)(spinal abnormalities present by birth) surgical repair
- Encepahaocles repair surgery.
-
- Vascular conditions and stroke surgeries: revascularization surgeries for moya moya disease.
- Pediatric brain and spine tumour surgeries.
-
- Pediatric brain and spine infection surgeries: Endoscopic and open surgeries for brain and spine infections.
- Pediatric traumatic brain and spinal injury.
- Antenatal counselling for congenital fatal neurosurgical conditions.