What is epilepsy?
Epilepsy is a chronic neurological condition marked by recurring, spontaneous seizures. Sudden, sensitive electrical discharges cause these seizures in a group of brain cells. The condition can affect people of all ages, and its severity can range from mild to disabling.
Causes and reasons for epilepsy:
- Genetic factors:
- Epilepsy is a condition characterized by genetic mutations that can impact the communication between neurons.
- Brain injuries:
- Epilepsy can develop years after head trauma from accidents or injuries, often due to the long-term effects of the injury.
- Neurological disorders:
- Epilepsy can be caused by stroke, brain tumours, and infections like meningitis or encephalitis, which damage brain tissue.
- Developmental disorders:
- Autism and neurofibromatosis are linked to a higher likelihood of epilepsy.
- Prenatal injury:
- Oxygen deficiencies, infections, and poor nutrition during pregnancy can significantly impact brain development and increase the possibility of epilepsy.
- Unknown causes:
- Idiopathic epilepsy refers to cases where the cause of epilepsy remains unknown.
Symptoms of epilepsy:
- Seizures:
- Focal (partial) seizures:
- A brain disorder affecting one part can result in sensory or motor symptoms, unusual sensations, or behavioural changes.
- Generalised seizures:
- This condition affects the entire brain and includes tonic-clonic seizures involving convulsions and loss of consciousness and absence seizures involving brief lapses in awareness.
- Auras:
- Some people may have auras, which are warning indications before a seizure, such as odd scents, tastes, or sensations.
- Loss of consciousness:
- Some seizures cause a loss of consciousness or awareness, and the sufferer may appear to stare blankly.
- Muscle spams and jerks:
- Sudden, uncontrollable muscle jerks (myoclonus) or sustained muscle stiffening (tonic seizures).
- Psychological symptoms:
- During seizures, some persons may suffer psychological symptoms, including fear and anxiety.
Diagnosis of epilepsy:
- Medical history and physical examination:
- Detailed seizure history and physical examination.
- Electroencephalogram (EEG):
- The brain’s electrical activity is recorded and is frequently utilized for diagnosing epilepsy.
- Neuroimaging:
- MRI or CT scans are utilized to detect brain structural abnormalities that may be causing seizures.
- Genetic testing:
- It can be useful for identifying specific genetic variants associated with epilepsy.
Treatment for epilepsy:
- Medications:
- Anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs): The primary treatment for seizures is based on medication selection, which is determined by the type of seizures and the child’s age.
- Surgery:
- Respective surgery: Seizures can be effectively treated by surgical removal of a specific area of the brain in cases where they originate from that area.
- Other surgical options: Severe cases may require procedures such as corpus callosotomy or hemispherectomy.
- Neurostimulation:
- Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS): A device implanted under the skin sends electrical impulses to the brain to decrease seizure frequency.
- Responsive neurostimulation (RNS): The implanted device monitors brain activity and provides stimulation to prevent seizures.
- Dietary therapies:
- Ketogenic diet: A diet containing high fat and low carbohydrates has been proven to reduce seizures in certain children effectively.
- Modified Atkins diet and low glycemic index treatment (LGIT): These are less restrictive alternatives to the ketogenic diet.
- Behavioural and supportive therapies:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and other psychological interventions can effectively manage the emotional and psychological impact of epilepsy.
- Supportive therapies, such as speech, occupational, and physical therapy, are used to address developmental delays and other related issues.
Management and prognosis:
- Regular monitoring:
- The continuous evaluation and modification of treatment plans are of utmost importance.
- Educational support:
- IEPs are often utilized by children with epilepsy to tackle their learning difficulties.
- Family and community support:
- Support groups and educational resources can assist families in managing their condition and enhancing their child’s quality of life.
Hyderabad, renowned for its cultural diversity and historical significance, is a hub for medical advancements, particularly in epilepsy treatment. With numerous healthcare facilities and specialists using the latest technologies, Hyderabad’s diverse cultural fabric is reflected in its inclusive healthcare system, catering to people from all backgrounds. The city’s multicultural blend of religions contributes to its varied healthcare system.
Hyderabad, a city known for its cultural diversity and medical innovation, is a top epilepsy treatment hub. Its advanced healthcare infrastructure, staffed by qualified professionals, ensures top-notch care. The city’s medical community’s inclusive approach demonstrates its commitment to improving health outcomes for its residents.
About Dr Vishakha
Dr. Vishakha Karpe, a highly skilled Senior Paediatric Neurosurgeon at Rainbow Children’s Hospital, Banjara Hills, and Hyder Nagar in Hyderabad, is one of India’s leading paediatric neurosurgeons with extensive experience in paediatric neurosurgery. With over nine years of dedicated practice, she is among the few in India working extensively in this field.
With extensive experience in paediatric neurosurgical conditions, she focuses on comprehensive care, including precise surgery and educating parents about the complete case management protocol. She is an efficient and passionate medical professional, pursuing ethical practice and ensuring patient care after surgery.
Proficiency of Dr Vishaka:
Hydrocephalus (increased fluid in the brain): The procedure involves an endoscopic third ventriculostomy and CSF diversion (VP shunt) to treat complex hydrocephalus.
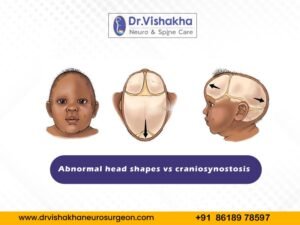
- Craniosynostosis (abnormal head shape due to untimely cranial sutures fusion) surgeries: Helmet therapy is a technique that is used in both endoscopic and open surgery.
- Spinal dysraphisms(Spina Bifida)- (spinal abnormalities present by birth) – surgical repair
- Encepahaocles repair surgery.
- Vascular conditions and stroke surgeries: revascularization surgeries for moya moya disease.
- Pediatric brain and spine tumour surgeries.
- Pediatric brain and spine infection surgeries: Endoscopic and open surgeries for brain and spine infections.
- Pediatric traumatic brain and spinal injury.
- Antenatal counselling for congenital fatal neurosurgical conditions.
Dr Vishaka specializes in craniosynostosis surgery, which is only done in a few centres in India. Dr Vishaka Patil, M.B.B.S, DNB (AIIMS) New Delhi, M.Ch (IPGMER SSKM) became a Member of “The Royal College of Surgeons, Edinburgh” (U.K.) a highly successful and best pediatric neurosurgeon in Hyderabad, Telangana with 13 years of experience, is among the topmost pediatric neurosurgeons in the Rainbow group of hospitals at Hyder Nagar and Banjara Hills.