Craniosynostosis is when one or more sutures in a baby’s skull close prematurely, affecting the head shape and brain development. The treatment comprises surgery to correct the shape of the skull and allow for proper brain growth. The timing and type of surgery depend on the severity and specific type of craniosynostosis. If treated early, children can have normal cognitive development and a good quality of life. Regular follow-up care with a medical team is crucial to monitor the child’s growth and address any issues. With proper treatment, most children with craniosynostosis can lead healthy, everyday lives.
What is craniosynostosis?
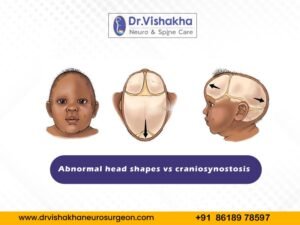
Craniosynostosis is a congenital condition in which the skull’s sutures close prematurely. This restricts skull growth and potentially increases brain pressure, leading to physical and developmental issues. Sutures are fibrous junctions between skull bones that allow the skull to expand as the brain grows.
Types of craniosynostosis and associated symptoms:

- Sagittal synostosis (scaphocephaly):
- Sagittal synostosis, or scaphocephaly, is a frequent craniosynostosis caused by premature fusion of the sagittal suture. This suture divides the skull’s left and right sides, restricting transverse growth and resulting in a long and narrow head.
- Coronal synostosis:
- Coronal synostosis is a disease characterised by the early fusion of coronal sutures, unilateral or bilateral, on one or both sides of the head.
- Metopic synostosis (trigonocephaly):
- Metopic synostosis, also known as trigonocephaly, is a condition marked by early fusion of the metopic suture. It affects the shape of the forehead and the overall facial appearance.
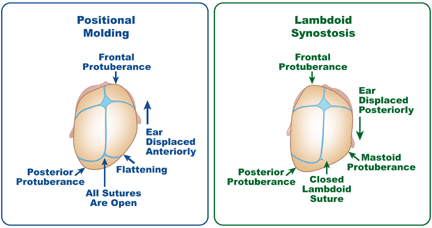
- Lambdoid synostosis:
- A lambdoid synostosis is a rare form of craniosynostosis involving premature fusion of the lambdoid suture. It can affect skull shape and potentially cause asymmetry.
Craniosynostosis is a congenital condition in which the skull’s sutures close prematurely. This restricts skull growth and potentially increases brain pressure, leading to physical and developmental issues. Sutures are fibrous junctions between skull bones that allow the skull to expand as the brain grows.
Reasons and causes of craniosynostosis in children:
- Genetic factors:
- Craniosynostosis is a genetic condition often linked to syndromes like Crouzon, Apert, and Pfeiffer. It is usually inherited as an autosomal dominant trait, which implies that only one parent can have the mutant gene.
- Environmental factors:
- Environmental factors during pregnancy, such as maternal smoking, advanced maternal age, and certain medications, may increase the risk.
- Sporadic occurrence:
- Craniosynostosis is frequently sporadic and not linked to any known cause or family history.
Diagnosis of craniosynostosis:
- Physical examination:
- Head shape: A paediatrician or specialist will scrutinise the baby’s head shape for any signs of craniosynostosis.
- Fontanelles: The doctor will examine the soft spots on the baby’s head, known as fontanelles, for potential abnormalities.
- Suture ridges: Ridges along the sutures may indicate early closure.
- Medical history:
- Family history: The doctor will ask about any family history of craniosynostosis or other genetic disorders.
- Pregnancy and birth history: The mother’s and baby’s birth provide additional context.
- Imaging studies:
- X-rays: These can initially evaluate the skull and suture lines.
- CT scan: CT scans provide a detailed skull image, providing a 3D view of sutures and bones, making them the gold standard for diagnosing craniosynostosis.
- MRI: This term is often used to evaluate brain structure and identify potential abnormalities or complications.
- Genetic testing:
- Blood tests: Blood tests are conducted to identify specific genetic mutations if a suspected genetic syndrome is suspected.
- Chromosomal analysis: This method can assist in identifying potential chromosomal abnormalities linked to craniosynostosis.
- Specialist consultation:
- Craniofacial specialist: A specialist in craniofacial anomalies may be consulted for further evaluation and treatment planning.
- Neurosurgeon: A pediatric neurosurgeon will be involved in the diagnosis and treatment planning if surgery is required.
- Treatment planning: A treatment plan, including surgical correction and regular follow-up care, is typically created.
Early diagnosis and intervention of craniosynostosis, typically within the first year of life, are crucial for successful treatment, preventing complications related to brain growth and development and ensuring healthy development.
Potential behavioural and developmental issues that may arise:
Children and babies with craniosynostosis may experience behavioural and developmental issues, varying based on severity, associated syndromes, and potential complications like increased intracranial pressure.
- Cognitive and developmental delays:
- Learning difficulties: Children with craniosynostosis may face learning and cognitive development challenges.
- Delayed milestones: Delays in achieving developmental milestones like sitting, crawling, walking, and talking may occur.
- Attention and hyperactivity:
- Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): Children with craniosynostosis may be at a higher risk for ADHD, characterised by attention difficulties, hyperactivity, and impulsiveness.
- Social and emotional challenges:
- Social interaction difficulties: Children may struggle with peer interaction, leading to social isolation or difficulty forming friendships.
- Emotional regulation: Emotional management issues can increase irritability, frustration, or mood swings.
- Behavioural issues:
- Aggression: Children may exhibit aggressive behaviours as a response to frustration or communication difficulties.
- Impulsivity: Individuals with problems with impulse control may engage in risky or inappropriate behaviours based on their age.
- Sensory processing issues:
- Sensory sensitivities: Children with craniosynostosis may exhibit increased sensitivity to sensory stimuli like loud noises, bright lights, or certain textures.
- Motor coordination: Motor skills and coordination difficulties can impact activities like handwriting, sports, and other physical tasks.
- Psychological impact:
- Self-esteem: Children with noticeable facial or skull differences may face self-esteem issues, leading to bullying or negative peer attention.
- Anxiety and depression: Medical procedures and social challenges can cause anxiety and depression in some children due to their stress and challenges.
Management and support:
- Early intervention programmes: These programs offer therapies and support to assist children in reaching their developmental milestones.
- Behavioural therapy: Cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) is a technique that aids in managing specific behavioural issues.
- Educational support: Special education services, individualised education plans (IEPs), and other educational supports can aid children in their learning process.
- Medical follow-up: Regular check-ups with healthcare providers like neurologists, psychologists, and developmental paediatricians can help monitor and address emerging issues.
- Family counselling: Counselling and support groups for families can offer practical strategies for managing behavioural challenges and providing emotional support.
Prognosis:
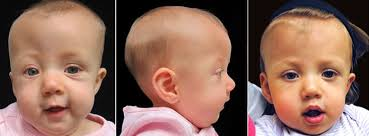
Early and appropriate treatment for craniosynostosis can lead to normal, healthy lives for most children. Regular monitoring and follow-up care are crucial for proper skull and brain development, minimising potential complications and intracranial pressure.
About Dr Vishakha
Dr. Vishakha Karpe, a highly skilled Senior Paediatric Neurosurgeon at Rainbow Children’s Hospital, Banjara Hills, and Hyder Nagar in Hyderabad, is one of India’s leading paediatric neurosurgeons with extensive experience in paediatric neurosurgery. With over nine years of dedicated practice, she is among the few in India working extensively in this field.
With extensive experience in paediatric neurosurgical conditions, she focuses on comprehensive care, including precise surgery and educating parents about the complete case management protocol. She is an efficient and passionate medical professional, pursuing ethical practice and ensuring patient care after surgery.
Proficiency of Dr Vishaka:
Hydrocephalus (increased fluid in the brain): The procedure involves an endoscopic third ventriculostomy and CSF diversion (VP shunt) to treat complex hydrocephalus.
- Craniosynostosis (abnormal head shape due to untimely cranial sutures fusion) surgeries: Helmet therapy is a technique that is used in both endoscopic and open surgery.
- Spinal dysraphisms(Spina Bifida)- (spinal abnormalities present by birth) – surgical repair
- Encepahaocles repair surgery.
- Vascular conditions and stroke surgeries: revascularization surgeries for moya moya disease.
- Paediatric brain and spine tumour surgeries.
- Paediatric brain and spine infection surgeries: Endoscopic and open surgeries for brain and spine infections.
- Paediatric traumatic brain and spinal injury.
- Antenatal counselling for congenital fatal neurosurgical conditions.
Dr Vishaka specialises in craniosynostosis surgery, which is only done in a few centres in India. Dr Vishaka Patil, M.B.B.S, DNB (AIIMS) New Delhi, M.Ch (IPGMER SSKM) became a Member of “The Royal College of Surgeons, Edinburgh” (U.K.) a highly successful and best paediatric neurosurgeon in Hyderabad, Telangana with 13 years of experience, is among the topmost paediatric neurosurgeons in the Rainbow group of hospitals at Hyder Nagar and Banjara Hills.