What is congenital brain and spinal malformation?
Congenital brain and spinal malformations are congenital disabilities that affect the brain, spine, and spinal cord’s structure and function. They can range from mild conditions to severe disabilities requiring medical intervention, typically present at birth.
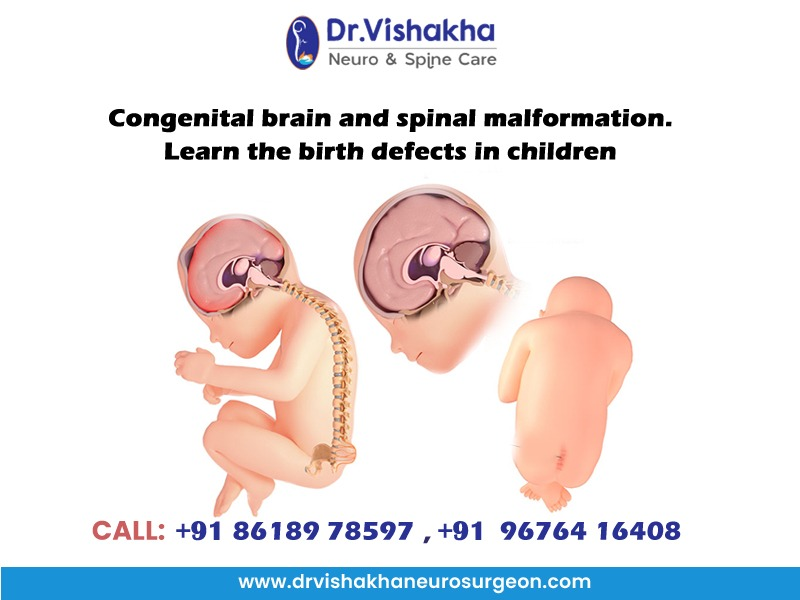
- Spina bifida is a congenital spinal malformation caused by incomplete vertebrae enclosing the spinal cord, resulting in a gap or opening in the spine. The severity varies, with the most severe form being myelomeningocele, which can cause paralysis, bladder and bowel control issues, and hydrocephalus, a fluid buildup in the brain. Symptoms include paralysis, leg weakness, and brain issues.
- Anencephaly is a severe neural tube defect causing significant neurological impairment, often leading to stillbirth or death in babies. This condition results in the loss of cognitive and motor functions in the remaining brain tissue. It is incompatible with life beyond a few hours or days, making it a critical issue for those affected.
- Hydrocephalus is a brain condition caused by an abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid, leading to increased pressure on the brain and potential brain damage. Symptoms include an enlarged head, vomiting, developmental delays, and seizures. Treatment usually involves surgically placing a shunt to drain excess fluid from the brain. The condition can be present at birth or develop later in childhood.
- Craniosynostosis is a condition where skull sutures fuse prematurely, causing abnormal head shapes and potentially restricting brain growth. Treatment often involves surgery to correct the skull shape and allow for proper brain development. The condition can result in developmental delays, intellectual disabilities, and potential brain development issues, depending on the type of suture closure.
- An encephalocele is a rare congenital disability where a portion of the brain protrudes through a skull opening, often at the back of the head. This sac-like structure, containing brain tissue and membranes, can cause developmental delays, neurological issues, and seizures in some cases. Children born with encephaloceles may require surgery to close the defect.
- Chiari malformation is a condition where brain tissue extends into the spinal canal, often due to an abnormally small or misshapen skull. Symptoms include headaches, neck pain, balance issues, difficulty swallowing, and paralysis. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to alleviate pressure on the brain and spinal cord, often linked to spina bifida.
- Holoprosencephaly is a brain defect that occurs during early fetal development, causing intellectual disabilities, facial abnormalities, and motor dysfunction. The severity depends on the extent of brain development failure. Many children with holoprosencephaly experience significant developmental delays and may face lifelong challenges, highlighting the importance of proper brain development.
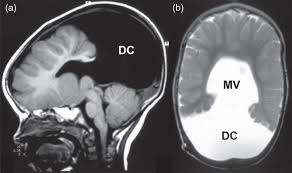
- Dandy-Walker syndrome is a congenital brain malformation affecting the cerebellum, responsible for balance and coordination. It results in developmental delays, motor problems, and coordination difficulties in children. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms, which may include physical therapy and, in some cases, surgical intervention. The syndrome is associated with an enlargement of the fourth ventricle and a cyst-like structure near the skull base.
- A tethered spinal cord is an abnormally attached part of the spinal column, limiting movement and causing symptoms such as back pain, leg weakness, bladder and bowel control issues, and developmental delays in children. Treatment often involves surgery to free the spinal cord from its tethered position, preventing further complications.
- Agenesis of the corpus callosum is a rare condition where the brain’s two hemispheres fail to develop, leading to developmental and neurological issues like intellectual disabilities, seizures, and motor coordination problems. Early intervention and therapy are crucial for managing this condition.
Causes and risk factors
A combination of genetic and environmental factors causes congenital brain and spinal malformations. Genetic mutations, family history of congenital disabilities, and certain inherited conditions increase the likelihood of a child being born with these defects. Environmental factors like toxins, drugs, infections, or malnutrition during pregnancy also contribute.
Diagnosis and early detection
Early detection of congenital brain and spinal malformations in pregnancy can be achieved through ultrasound imaging, with additional diagnostic tests like MRI or CT scans used post-birth for more detailed assessment. Amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling may be recommended if genetic factors are suspected.
Treatment and prevention
Congenital brain and spinal malformations can be treated based on the severity and child’s age. Treatment options include surgery to correct structural issues, physical and occupational therapy to improve motor function and development, medications for conditions like hydrocephalus, and supportive care to manage developmental delays and associated symptoms. Preventative measures like folic acid supplements during pregnancy can reduce the risk of congenital disabilities like spina bifida and anencephaly. Surgery may be necessary for physical malformations like spina bifida or craniosynostosis, while physical and occupational therapy improves development and motor function. Lifelong care may be necessary for developmental delays, motor coordination, and neurological function. Preventative measures include folic acid supplementation, avoiding alcohol, tobacco, and certain medications, and regular prenatal care and screening.
Congenital brain and spinal malformations are a significant concern for parents, healthcare providers, and society. Advances in medical technology, surgical procedures, and supportive therapies have improved the prognosis for children born with these defects. However, further research and awareness are needed to improve outcomes and support affected families in providing the best care.
About Dr Vishakha: Dr Vishakha Basavraj Karpe is a highly skilled senior consultant at Rainbow Children’s Hospital in Banjara Hills and Hydernagar Hyderabad. She is known for her comprehensive care approach and is one of the few dedicated leading paediatric neurosurgeons in the city and India with over ten years of extensive experience in pediatric neurosurgery. Her expertise includes treating hydrocephalus, spinal dysraphism, craniosynostosis, paediatric brain infections, brain and spine tumours and stroke surgery.
She has a special interest in craniosynostosis surgery, which is done only in very few centres in India.
Proficiency of Dr Vishakha:
-
- Hydrocephalus (increased fluid in the brain): The procedure involves an endoscopic third ventriculostomy and CSF diversion (VP shunt) to treat complex hydrocephalus.
- Craniosynostosis (abnormal head shape due to untimely cranial sutures fusion) surgeries: Helmet therapy is a technique that is used in both endoscopic and open surgery.
- Spinal dysraphisms(Spina Bifida)- (spinal abnormalities present by birth) – surgical repair
- Encepahaocles repair surgery.
-
- Vascular conditions and stroke surgeries: revascularization surgeries for moya moya disease.
- Pediatric brain and spine tumour surgeries.
-
- Pediatric brain and spine infection surgeries: Endoscopic and open surgeries for brain and spine infections.
- Pediatric traumatic brain and spinal injury.
- Antenatal counselling for congenital fatal neurosurgical conditions.