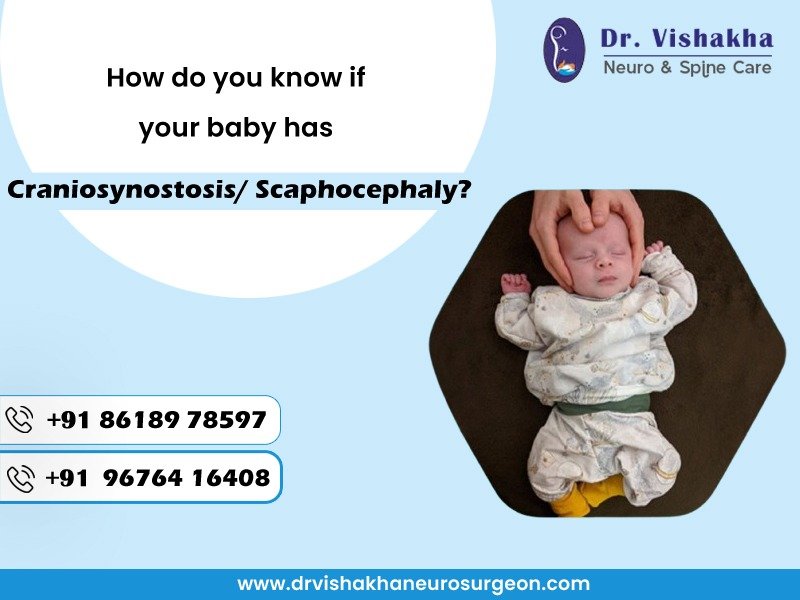
When the connective tissue in a baby’s brain and skull closes prematurely, craniosynostosis occurs. This limits extension in certain ranges, pushing the cranium into irregular shapes. A child may have craniosynostosis, particularly scaphocephaly, if they have a strangely formed head, such as a long and contract head with an unmistakable edge along the best, moderate head development, and a bizarre facial appearance, depending on the seriousness of the condition.
I am Dr Vishakha Karpe, a senior pediatric neurosurgeon specialist at Rainbow Children’s Clinic in Hyderabad; I offer surgical and non-surgical medications for Craniosynostosis/Scaphocephaly based on the child’s side effects, seriousness, and well-being conditions. Early mediation anticipates complications like expanded weight, formative delays, or critical cranium deformation. The adequacy of surgeries is decided by variables such as age, seriousness, and combined suture location.
Surgical and non-surgical medications point to progress in cranium shape, diminish brain weight, and advance ordinary improvement. An interview with a paediatrician is required to watch for side effects and refer the child to a pediatric neurosurgeon or craniofacial specialist.

Key signs to screen for Craniosynostosis/ Scaphocephaly include:
Ridges on the skull
An unmistakable edge along intertwined sutures is a vital sign of craniosynostosis, where the sutures between cranium bones are more often than not delicate and adaptable in newborn children. Still, if they intertwine rashly, a rough edge may appear.
Missing or little delicate spot (Fontanelle)
The fontanelle, a delicate spot on a baby’s head, regularly remains open until 18 months. In any case, babies with craniosynostosis may near as well early or not exist, causing trouble in cranium extension amid brain growth.
Slower head growth
Doctors determine a baby’s head circumference amid pediatric visits to track development. Untimely suture closure can cause the head to halt developing or develop slower than the body, regularly demonstrating craniosynostosis.
Facial asymmetry
Premature suture combination can change facial symmetry, driving to unmistakable temples, more critical or higher eye attachments, and uneven noses or misaligned jaws. In a few cases, this can influence the midface, coming about in an uneven nose or misaligned jaw.
Developmental delays
Craniosynostosis can cause formative delays in babies due to confined brain development, causing slower points of reference like sitting, slithering, or strolling. In any case, not all cases result in delays due to expanded intracranial weight on the interior of the skull.
Eye and vision problems
Fused sutures or anomalous cranium shapes can cause eye situating issues, such as bulging eyes, strabismus, and vision issues. Proptosis alludes to the appearance of eyes bulging outward, whereas strabismus happens when eyes do not move legitimately. Expanded weight can lead to optic nerve damage.
Surgical treatments:
Cranial vault renovating (CVR)
Skull reshaping surgery is a conventional method that includes expelling, reshaping, and repositioning intertwined cranium bones to advance appropriate brain development and a normal head shape. Regularly performed between 6 and 12 months of age, it requires an entry point over the scalp and can take a few weeks to recover.
Endoscopic surgery
Endoscopic surgery is a negligibly obtrusive strategy for newborn children under six months old. The strategy involves evacuating a melded suture to reshape the cranium as the brain develops. When compared to conventional surgery, it has a few preferences, including shorter working times, less blood misfortune, and quicker recuperation. After the method, the infant is, as a rule, fitted with a custom-made shaping helmet.
Spring-assisted surgery
This is another negligibly intrusive choice where springs are embedded to offer assistance to extend the cranium over time. The springs are evacuated after a few months. This is less common but is utilized in select cases.
Distraction osteogenesis:
Distraction gadgets are utilized to steadily extend bones and make brain development space for complex cranium deformations or noteworthy cranium developments, especially when an expansive parcel of the cranium needs expansion.
Non-surgical treatments:
Helmet treatment (cranial orthosis)
Helmet treatment is prescribed for mellow cases of positional plagiocephaly to shape the cranium as it develops. In any case, it is incapable of craniosynostosis or scaphocephaly once sutures combine rashly. It is frequently prescribed after endoscopic surgery to direct the cranium into the adjusted shape amid recuperation. The seriousness of the cranium deformation and the baby’s age decide how long he or she must wear the helmet.
Doctors may prescribe perception in mellow cases of craniosynostosis or newborn children with negligible brain development effects, but most cases require surgery for appropriate brain and cranium improvement.
About Dr Vishakha
Dr. Vishakha Karpe, a highly skilled Senior Paediatric Neurosurgeon at Rainbow Children’s Hospital, Banjara Hills, and Hyder Nagar in Hyderabad, is one of India’s leading paediatric neurosurgeons with extensive experience in paediatric neurosurgery. With over nine years of dedicated practice, she is among the few in India working extensively in this field.
With extensive experience in paediatric neurosurgical conditions, she focuses on comprehensive care, including precise surgery and educating parents about the complete case management protocol. She is an efficient and passionate medical professional, pursuing ethical practice and ensuring patient care after surgery.
Proficiency of Dr Vishaka:
Hydrocephalus (increased fluid in the brain): The procedure involves an endoscopic third ventriculostomy and CSF diversion (VP shunt) to treat complex hydrocephalus.
- Craniosynostosis (abnormal head shape due to untimely cranial sutures fusion) surgeries: Helmet therapy is a technique that is used in both endoscopic and open surgery.
- Spinal dysraphisms(Spina Bifida)- (spinal abnormalities present by birth) – surgical repair
- Encepahaocles repair surgery.
- Vascular conditions and stroke surgeries: revascularization surgeries for moya moya disease.
- Pediatric brain and spine tumour surgeries.
- Pediatric brain and spine infection surgeries: Endoscopic and open surgeries for brain and spine infections.
- Pediatric traumatic brain and spinal injury.
- Antenatal counselling for congenital fatal neurosurgical conditions.
Dr Vishaka specializes in craniosynostosis surgery, which is only done in a few centres in India. Dr Vishaka Patil, M.B.B.S, DNB (AIIMS) New Delhi, M.Ch (IPGMER SSKM) became a Member of “The Royal College of Surgeons, Edinburgh” (U.K.) a highly successful and best pediatric neurosurgeon in Hyderabad, Telangana with 13 years of experience, is among the topmost pediatric neurosurgeons in the Rainbow group of hospitals at Hyder Nagar and Banjara Hills.