Dr Vishakha K. – Senior consultant pediatric neurosurgeon, Hyderabad, India
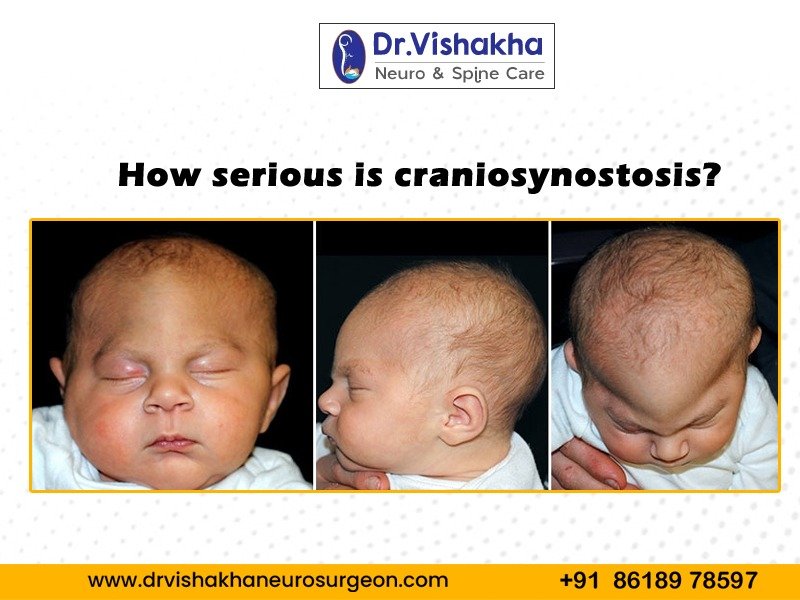
Craniosynostosis is the untimely closure of cranial sutures, which causes skull and brain development issues in babies. The severity varies depending on the number of sutures, other medical conditions, and specific types.
Craniosynostosis may trigger numerous issues:
- Cosmetic and functional impact:
- Skull deformity, characterized by abnormal skull and facial shape, can significantly impact an individual’s appearance and potentially lead to psychosocial issues.
- Abnormal skull shape and increased intracranial pressure can cause vision problems like strabismus, proptosis, and optic nerve damage.
- Craniosynostosis can cause hearing loss due to its impact on the ear’s structure, resulting in conductive or sensorineural hearing loss.
- Abnormal facial structure, especially in syndromic cases, can lead to respiratory issues like obstructive sleep apnea.
- Abnormal jaw alignment can result in malocclusion, a misaligned tooth, and other dental problems.
- Developmental issues : Cognitive impairment , speech issues, learning disabilities
- Intracranial pressure: The skull’s inability to expand properly can cause increased intracranial pressure, leading to symptoms like headaches, irritability, vomiting, developmental delays, cognitive impairments, and vision problems, necessitating early intervention.
Types of craniosynostosis :
Depending upon which and how many sutures are involved, and presence or absence of genetic abnormality , it is sub categorized into …
Single-suture craniosynostosis: The most common and least severe type involves the premature fusion of a single suture.
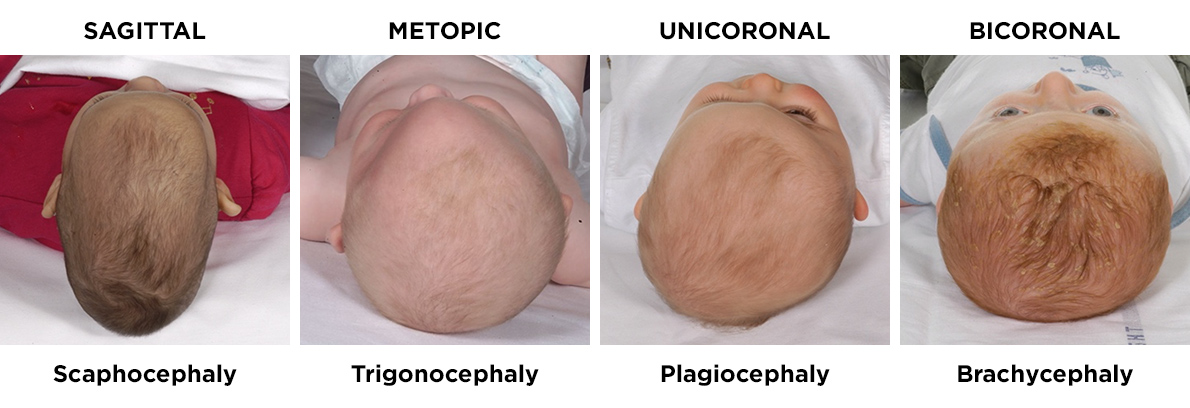
- Sagittal synostosis is the premature fusion of the sagittal suture, which results in a long and narrow head shape known as scaphocephaly.
- Coronal synostosis is the premature fusion of coronal sutures, which can cause asymmetry (plagiocephaly) or a short and broad head shape (brachycephaly), depending on the type of suture.
- Metopic synostosis is a premature fusion of the metopic suture, causing a triangular forehead (trigonocephaly) from the nose to the head.
- Lambdoid synostosis is a rare type of head shape caused by premature fusion of the lambdoid suture in the back of the head.
- Complex or multiple-suture craniosynostosis: Complex or multiple-suture craniosynostosis: This condition includes the untimely combination of numerous sutures and is ordinarily more serious than single-suture craniosynostosis. Complex Craniosynostosis involves fused multiple sutures, which cause significant skull deformities and increased intracranial pressure. The head shape varies based on the suture combination.
- Syndromic craniosynostosis: This type of genetic syndrome, often linked to physical and developmental abnormalities, is severe and complex, necessitating multidisciplinary medical management.
- Apert Syndrome is a condition marked by premature fusion of multiple sutures, syndactyly (flux of fingers and toes), and other skeletal abnormalities.
- Crouzon Syndrome is a condition characterized by craniosynostosis, midfacial hypoplasia, dental issues, and potential hearing loss.
- Pfeiffer Disorder is characterized by craniosynostosis, wide and brief thumbs and toes, and fractional delicate tissue syndactyly.
- Muenke Syndrome is a condition primarily characterized by coronal synostosis, which can lead to hearing loss and hand and foot abnormalities.
- Saethre-Chotzen Syndrome is a condition characterized by craniosynostosis, ptosis, facial asymmetry, and mild to moderate limb abnormalities.
Diagnosis of craniosynostosis:
A healthcare provider conducts a thorough physical examination of a baby’s head to identify abnormalities such as skull shape, asymmetry, and premature suture closure. They also measure head circumference and compare it to standard growth charts. A developmental assessment evaluates the baby’s milestones to identify delays due to increased intracranial pressure or brain development issues. Various imaging techniques, such as skull X-rays, CT scans, 3D reconstruction, and MRI, are used to confirm the diagnosis, to assess brain structures and rule out other potential issues. Genetic counseling and testing may be recommended for syndromic forms of craniosynostosis based on physical findings or family history. Blood samples and panel testing can detect specific genetic mutations.
Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and management, preventing complications like increased intracranial pressure, developmental delays, and cosmetic deformities.
A multidisciplinary team develops an individualized treatment plan, which may involve surgery to correct skull shape and average brain growth. Regular follow-ups are necessary to monitor the child’s development and address any outstanding issues.
Early diagnosis and treatment of craniosynostosis are crucial for minimizing its impact on brain development and overall health. Delayed diagnosis can result in severe complications such as increased intracranial pressure and cosmetic deformities
Importance of identifying risk factors:
1.Genetic factors: Craniosynostosis is a genetic condition characterized by cranial deformities, often linked to gene mutations. It can be part of genetic syndromes like Apert, Crouzon, Pfeiffer, Muenke, and Saethre-Chotzen, which are often inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. In some cases, genetic mutations causing craniosynostosis can occur spontaneously, not inherited from the parents.
2.Environmental factors: Maternal smoking during pregnancy may increase the risk of craniosynostosis, while advanced maternal and paternal age may increase the likelihood of genetic mutations in the sperm or egg.
Certain medications, such as fertility treatments and anti-seizure medications, have been linked to a higher risk of craniosynostosis.
Maternal health conditions, such as thyroid disease, have also been associated with an increased risk.
3.Prenatal factors: Some evidence suggests premature birth may also increase the risk.
Treatment and prognosis:
The treatment includes surgery to rectify the cranium shape and to create the space for growth of the brain.
Type of surgery depends on the age of the child at the presentation.
If presented early, between 3 to 6 months of age, less invasive endoscopic assisted surgery can be offered.
Early surgery can prevent brain growth issues, developmental delays and cognitive issues. With timely and appropriate treatment, many children with craniosynostosis can lead healthy lives with normal cognitive development. However, ongoing medical follow-up is necessary to monitor and manage potential complications or associated conditions. Multidisciplinary care often involves a team of specialists. Regular monitoring is crucial to address any ongoing issues related to growth, development, and overall health. Early and effective treatment can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the risk of long-term complications.
This rare condition can be managed effectively, allowing affected individuals to lead healthy, productive lives. About Dr Vishakha Karpe :
Dr. Vishakha Karpe, a highly skilled Senior Paediatric Neurosurgeon at Rainbow Children’s Hospital, Banjara Hills, and Hyder Nagar in Hyderabad, is one of India’s leading paediatric neurosurgeons with extensive experience in paediatric neurosurgery. With over ten years of dedicated practice, she is among the few in India working extensively and exclusively in this field. She has keen interest in craniosynostosis surgery.
She focuses on comprehensive care, including precise surgery and educating parents about the complete case management protocol.
Proficiency of Dr Vishakha:
Hydrocephalus (increased fluid in the brain): The procedure involves an endoscopic third ventriculostomy and CSF diversion (VP shunt) to treat complex hydrocephalus.
- Craniosynostosis (abnormal head shape due to untimely cranial sutures fusion) surgeries: Helmet therapy is a technique that is used in both endoscopic and open surgery.
- Spinal dysraphisms(Spina Bifida)- (spinal abnormalities present by birth) – surgical repair
- Encepahaocles repair surgery.
- Vascular conditions and stroke surgeries: revascularization surgeries for moya moya disease.
- Pediatric brain and spine tumour surgeries.
- Pediatric brain and spine infection surgeries: Endoscopic and open surgeries for brain and spine infections.
- Pediatric traumatic brain and spinal injury.
- Antenatal counselling for congenital fatal neurosurgical conditions.