
Hydrocephalus Treatment in Hyderabad | Dr Vishakha
Hydrocephalus is a medical condition where cerebrospinal fluid ( CSF) accumulates in the brain’s ventricles, increasing intracranial pressure. This imbalance can compress brain tissue and cause brain damage and developmental delays. It can be congenital or acquired due to developmental abnormalities or conditions like tumors, infections, brain bleeding, or head injuries.

What is Hydrocephalus?
Hydrocephalus is a medical condition involving the abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the brain’s ventricles, causing an imbalance between its production and absorption, resulting in increased pressure within the brain. Hydrocephalus can be congenital or acquired condition. It can be caused by developmental abnormalities, tumors, infections, or brain bleeding and may require medical intervention.
What is cerebrospinal fluid?
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a vital fluid enclosing the brain and spinal cord, vital for maintaining the health and proper functioning of the central nervous system.
Key function of cerebrospinal fluid:
- Protection:
- It serves as a support system for the spinal cord and brain.
- It provides a buoyant environment that helps support the brain’s weight, preventing it from pressing against the skull.
- Buoyancy:
- The brain is immersed in CSF, which helps reduce its effective weight by about 95%.
- This buoyancy prevents the brain from being compressed under its weight, especially when a person is upright.
- Shock absorption:
- CSF acts as a shock absorber, protecting the brain and spinal cord from sudden movements or impacts.
- This function is essential for preventing damage to delicate neural tissues.
- Nutrient transport:
- CSF transports nutrients, such as glucose, from the blood to the brain and removes waste products brain cells produce.
- This transport helps maintain the proper chemical environment for neuronal function.
- Removal of waste:
- CSF plays a role in removing waste products and metabolic byproducts from the brain.
- These waste materials are then transported away from the CNS and eventually absorbed into the bloodstream.
- Temperature regulation:
- CSF aids in the regulation of brain temperature, preventing overheating.
- It acts as a heat exchange medium, dissipating excess heat produced by metabolic processes in the brain.
- Protection against infections:
- CSF acts as a barrier that helps protect the brain and spinal cord from certain infections.
- The blood-brain barrier, formed by the choroid plexus and the capillaries in the brain, helps prevent harmful substances and pathogens from entering the CNS.
- Maintenance of intracranial pressure:
- CSF plays a role in maintaining a stable intracranial pressure within the skull.
- Changes in the volume of CSF can affect this pressure, and disruptions in CSF flow can lead to conditions such as hydrocephalus.
The brain’s ventricular system produces cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) through the choroid plexus, which circulates through the ventricles and subarachnoid space, ensuring the central nervous system’s health.
What is a ventricular system in the brain?
The ventricular system in the brain is a network of interconnected ventricles filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Overview of the ventricular system:
- Lateral ventricles:
The lateral ventricles are the two largest C-shaped cavities in the brain that are part of the ventricular system, which circulates cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Each ventricle consists of a frontal horn, a body, an atrium, and two posterior horns (occipital and temporal). They are crucial for containing and producing CSF and are connected to the third ventricle via the interventricular foramina of Monro.
- Third ventricle:
The midline cavity between the diencephalon’s two thalamic halves is connected to the lateral ventricles via the interventricular foramina and the fourth ventricle through the cerebral aqueduct.
- Cerebral aqueduct:
The Sylvius aqueduct, also known as the cerebral aqueduct, connects the third and fourth ventricles through the midbrain, facilitating the flow of cerebrospinal fluid.
- Fourth ventricle:
The fourth ventricle in the hindbrain communicates with the third ventricle via the cerebral aqueduct and exits the ventricular system through lateral and median apertures.
Cerebrospinal Fluid Production and Movement:
- Cerebrospinal fluid is produced by the choroid plexus, specialized structures within the ventricles that consist of a network of blood vessels and ependymal cells.
- The choroid plexus produces CSF, which flows through the ventricular system, nourishing the brain and removing waste products.
- CSF circulates through the ventricles and into the subarachnoid space surrounding the brain and spinal cord.
- Excess CSF is eventually absorbed into the bloodstream through structures called arachnoid villi or granulations.
Causes of hydrocephalus:
Hydrocephalus can be caused by both congenital and acquired factors, occurring at different life stages and presenting at birth.
Congenital causes:
Developmental abnormalities:
Infants may be born with congenital anomalies that affect the development of the central nervous system, including the ventricular system, and disrupt the normal flow of cerebrospinal fluid.
- Genetic factors:
Certain genetic conditions, such as those linked to brain development abnormalities and CSF circulation issues, can heighten the likelihood of hydrocephalus.
- Neural tube defects:
Spina bifida, a condition where the neural tube isn’t fully closed during fetal development, can be linked to hydrocephalus, a complex disorder with various causes. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial for managing hydrocephalus, which requires ongoing medical attention and an understanding of its reasons.
Expert Hydrocephalus Treatment in Hyderabad: Dr Vishakha Basavraj Karpe
Hydrocephalus—often referred to as ” water on the brain”—is a serious medical condition where an excess of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) builds up in the brain’s cavities (ventricles). This accumulation creates harmful pressure on brain tissues, requiring specialised surgical intervention to prevent long-term damage.
If you are seeking world-class care, Dr Vishakha Basavraj Karpe offers advanced surgical solutions for hydrocephalus in Hyderabad.
What is Hydrocephalus?
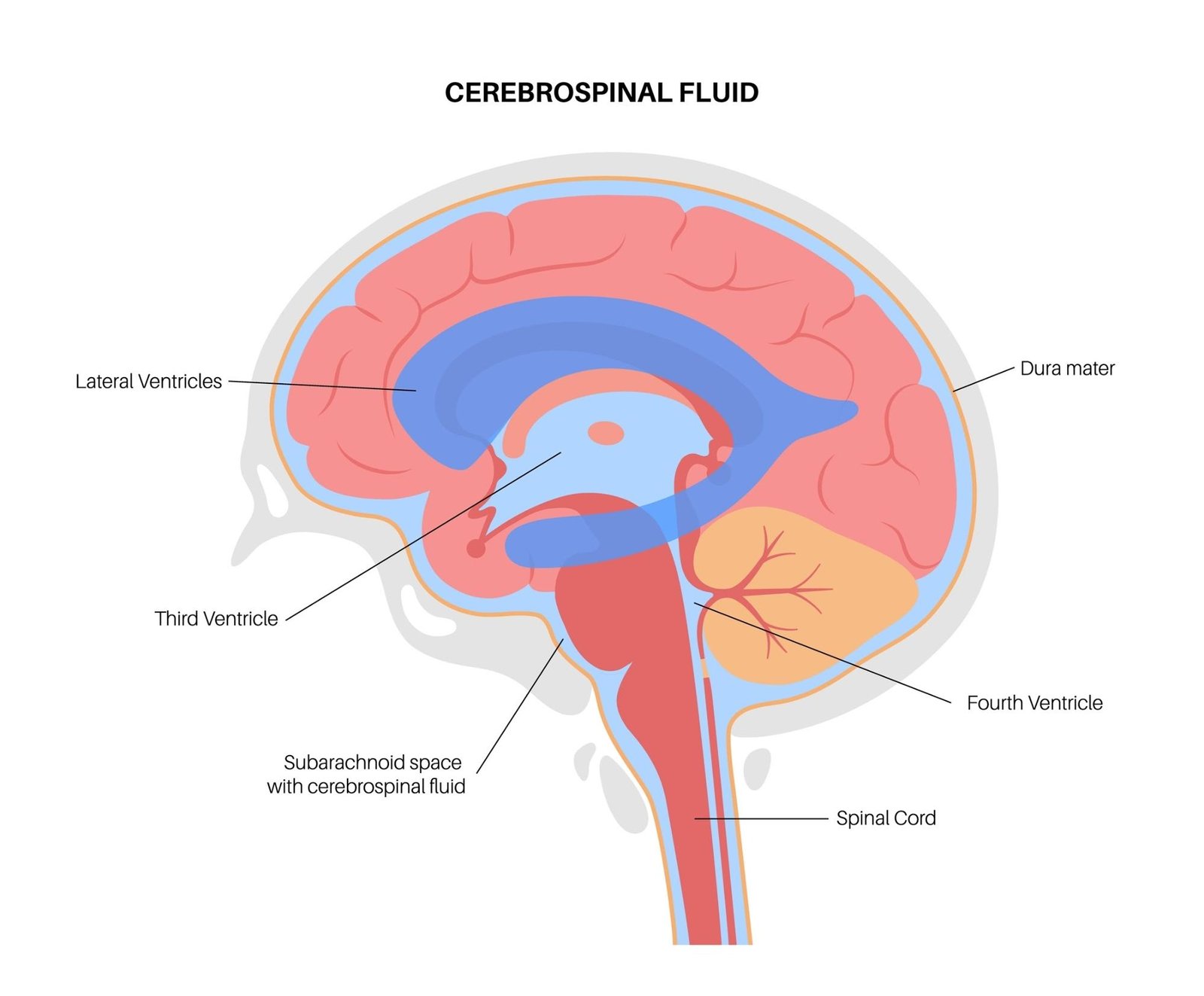
Hydrocephalus is derived from the Greek words “hydro” (water) and “cephalus” (head). While it is often described as “water on the brain,” the fluid is actually Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF).
Under normal conditions, CSF circulates through the brain’s ventricles, bathes the brain and spinal cord, and is absorbed into the bloodstream. When this circulation is disrupted, the fluid accumulates, causing the ventricles to enlarge and the pressure inside the head to increase.
Why Does It Happen? (Primary Reasons)
Hydrocephalus occurs due to an imbalance between how much CSF is produced and how much is absorbed into the bloodstream. The three most common reasons for this imbalance are:
- Obstruction (Non-communicating)
The most common cause. A physical blockage prevents CSF from flowing from one ventricle to another or into the spaces around the brain.
Common causes: Aqueductal stenosis (narrowing of a small passage in the brain), tumours, or cysts.
- Poor Absorption (Communicating)
The fluid can flow freely between the ventricles, but the “drainage sites” (arachnoid villi) are unable to absorb the fluid back into the blood.
Common causes: Often related to inflammation following infections like meningitis or bleeding (hemorrhage) in the brain.
- Overproduction
In very rare cases, the brain produces CSF faster than the body can possibly clear it.
Common cause: A rare type of non-cancerous tumour called a choroid plexus papilloma.
Types of Hydrocephalus
Understanding the specific type is crucial for Dr. Vishakha to determine the best surgical approach:
Congenital: Present at birth; caused by complex environmental and genetic factors during fetal development.
Acquired: Develops at the time of birth or at some point afterwards. This can affect people of all ages.
Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (NPH): Primarily affects older adults. It is unique because the pressure may remain near normal, but the fluid buildup causes a classic triad of symptoms: difficulty walking, cognitive decline, and urinary urgency.
Why Choose Dr. Vishakha?
Dr. Vishakha is a highly distinguished Senior Pediatric Neurosurgeon with over 15 years of experience. Her training from premier institutions like AIIMS (New Delhi) and IPGMER (Kolkata), Gold Medalist in MCh Neurosurgery combined with her international credentials (MRCS, Edinburgh), makes her a trusted name in complex neurosurgery.
Specialist in Neuroendoscopy: She has vast experience in Minimally invasive techniques for faster recovery.
Comprehensive Care: Expertise in both congenital (present at birth) and acquired hydrocephalus.
Dr. Vishakha utilisess state-of-the-art technology to provide the most effective treatment based on the patient’s specific condition:
- Ventriculoperitoneal (VP) Shunt
This is the most common treatment. A thin, flexible tube (shunt) is surgically implanted to divert excess CSF from the brain to the abdominal cavity, where the body safely absorbs it.
Best for: Most types of communicating and non-communicating hydrocephalus.
- Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy (ETV)
A minimally invasive procedure where Dr. Vishakha uses a neuroendoscope (a tiny camera) to create a small opening in the floor of the third ventricle. This allows the fluid to bypass the obstruction and flow naturally.
Benefits: No permanent hardware (shunts) left in the body; lower risk of long-term infection.
Symptoms to Watch For
Early diagnosis is critical. If your child or a loved one exhibits the following, consult Dr. Vishakha immediately:
In Infants: Unusually large head size, a rapid increase in head circumference, or a “sunsetting” appearance of the eyes (eyes gazing downward).
In Children/Adults: Persistent headaches, nausea, blurred vision, balance issues, or sudden changes in personality or cognitive function.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How is hydrocephalus diagnosed?
It is diagnosed using advanced neuroimaging to confirm a diagnosis:
Ultrasound: Primarily for infants through the “soft spot” on the head.
MRI: Provides the most detailed images of brain structures and fluid pathways.
CT Scan: A quicker way to view the size of the ventricles, often used in emergencies.
Is surgery the only option?
In the vast majority of cases, yes. Hydrocephalus is a mechanical problem that requires a mechanical solution—either a VP Shunt to divert the fluid or an ETV (Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy) to create a new drainage hole. Medication is rarely effective as a long-term solution.
What are the risks of the surgery?
As with any neurosurgery, there are risks, including infection, bleeding, or shunt malfunction. However, proper and advanced surgical techniques and experienced hands reduce these risks and speed up recovery times.
Can hydrocephalus be cured?
While hydrocephalus is a lifelong condition that requires ongoing monitoring, the symptoms can be successfully managed. Many patients treated by Dr. Vishakha goes on to lead full, active, and high-achieving lives.
What are the emergency “red flags” after treatment?
You should seek immediate medical attention if you notice:
Redness or swelling along the shunt tubing.
Persistent vomiting without a clear cause.
Suddenly, extreme sleepiness or inability to wake up.
A return of the original symptoms (severe headaches, blurred vision).
Proficiency of Dr Vishaka:
- Hydrocephalus (increased fluid in the brain) Treatment:
Endoscopic third ventriculostomy and CSF diversion (VP shunt) , neuroendoscopic
procedures for complex hydrocephalus. - Craniosynostosis (abnormal head shape due to untimely cranial sutures fusion) :
- Treatment –
Helmet therapy , endoscopic and open surgery. - Spinal dysraphisms(Spina Bifida)-
(spinal abnormalities present since birth) – surgical repair - Encephalocele repair surgery.
- Vascular and stroke surgeries:
revascularization surgeries for moya moya disease, emergency surgery for stroke - Pediatric brain and spine tumour surgeries.
- Pediatric brain and spine infection surgeries:
Endoscopic and open surgeries for brain and spine infections. - Pediatric traumatic brain and spinal injury.
- Antenatal counselling for congenital fatal neurosurgical conditions.
Dr Vishakha Karpe M.B.B.S, DNB (AIIMS) New Delhi, M.Ch (IPGMER SSKM) Member of “The Royal College of Surgeons, Edinburgh” (U.K.) is a highly competent and one of the best pediatric neurosurgeons in Hyderabad, Telangana with 13 years of experience, is among the topmost pediatric neurosurgeons in the Rainbow group of hospitals at Banjara Hills and Hyder Nagar.

