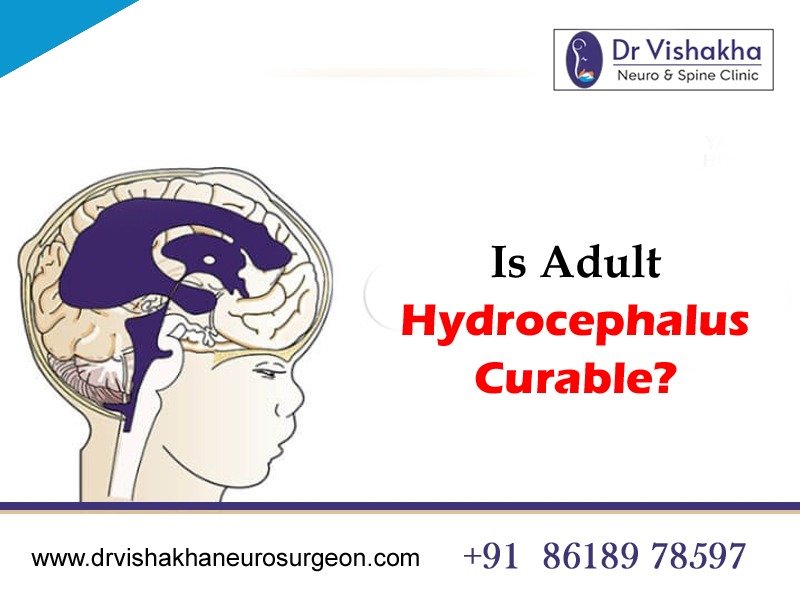
Hydrocephalus is a brain condition that can be managed and treated, but its curability depends on factors such as the underlying cause, severity, and individual response to treatment. Treatment options include surgical procedures to alleviate fluid buildup in the brain, such as shunts or endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV). Individuals with hydrocephalus should work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalised treatment plan.
Diagnosis is possible at any age, but young and middle-aged adults are more complex due to differences between infancy and childhood hydrocephalus and normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH). This age group faces challenges beyond routine medical care, including psychosocial, emotional, and occupational issues.
Undiagnosed hydrocephalus can remain dormant for years, with some people not noticing symptoms until adolescence or adulthood. Asymptomatic hydrocephalus may be identified on CT or MRI scans for unrelated neurologic symptoms headaches, or dizziness due to unrelated problems.
Undiagnosed hydrocephalus can lead to fluid buildup in the brain, affecting normal function or fluid spaces in the brain becoming more prominent over time, weakening the brain’s ability to compensate.
Diagnosis of hydrocephalus in adults
- Medical history:
The doctor will assess the individual’s symptoms, including headaches, cognitive changes, walking difficulties, urinary incontinence, and other signs linked to elevated intracranial pressure.
- Physical examination:
The doctor will conduct a neurological examination to evaluate the motor function, reflexes, coordination, and sensory function, potentially detecting signs of increased intracranial pressure like papilledema.
- Imaging studies:
- CT scan (computed tomography): This technology can offer detailed brain images and detect abnormalities like enlarged ventricles.
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging): MRI offers more detailed brain images than CT scans, often used to confirm hydrocephalus diagnosis and assess its severity.
- Intracranial pressure monitoring: Intracranial pressure monitoring is used in cases of uncertain diagnosis or hydrocephalus severity, involving a device inside the skull to measure pressure levels over time.
- Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF):If hydrocephalus is suspected due to infection or other underlying conditions, a cerebrospinal fluid sample can be obtained through a spinal tap and analysed for abnormalities.
The healthcare team diagnoses a condition and devises a treatment plan based on the cause, symptoms, and patient factors, which may involve medical management, surgery, or a combination of both, with regular follow-ups for monitoring and adjustments.
Most common causes and symptoms of hydrocephalus in adults:
-
Obstructive hydrocephalus:
- Tumours: Brain tumours, both primary and metastatic, can impede cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flow, resulting in hydrocephalus.
- Cysts: Colloid or arachnoid cysts in the brain can obstruct the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), leading to hydrocephalus.
- Congenital malformations: Birth-related conditions like aqueductal stenosis or Chiari malformation can impede cerebral blood supply, leading to hydrocephalus.
- Traumatic brain injury: Head trauma can lead to hydrocephalus, a condition characterised by bleeding, swelling, or damage to the structures responsible for CSF circulation.
-
Communicating hydrocephalus:
- Subarachnoid haemorrhage: Bleeding into the subarachnoid space, often due to a ruptured cerebral aneurysm, can disrupt CSF absorption and circulation, leading to a communicating hydrocephalus.
- Meningitis: Meningeal inflammation, affecting the brain and spinal cord membranes, can hinder CSF absorption and circulation, resulting in hydrocephalus.
- Idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (iNPH): Idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus, a condition characterised by gait disturbances, urinary incontinence, and cognitive decline, often occurs in older adults with unknown causes.
Symptoms:
- Headaches: Hydrocephalus is a common condition characterised by persistent headaches, often worsened in the morning or lying down, frequently accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
- Changes in mental status: Hydrocephalus can impact cognitive function, causing confusion, concentration issues, memory issues, and personality or behaviour changes.
- Gait disturbances: Hydrocephalus is a condition characterised by difficulty walking, imbalance, and a shuffling gait, with some individuals experiencing frequent falls or unsteadiness.
- Blurred vision: Hydrocephalus can cause vision issues like blurred vision, double vision (diplopia), or difficulty focusing due to pressure on the optic nerves.
- Urinary incontinence: Individuals with hydrocephalus may experience difficulty controlling urination, which may include increased frequency, urgency, or involuntary leakage.
Is hydrocephalus curable in adults?
Hydrocephalus, a condition that may not always be curable, can be effectively managed using various treatments.
-
Surgical intervention:
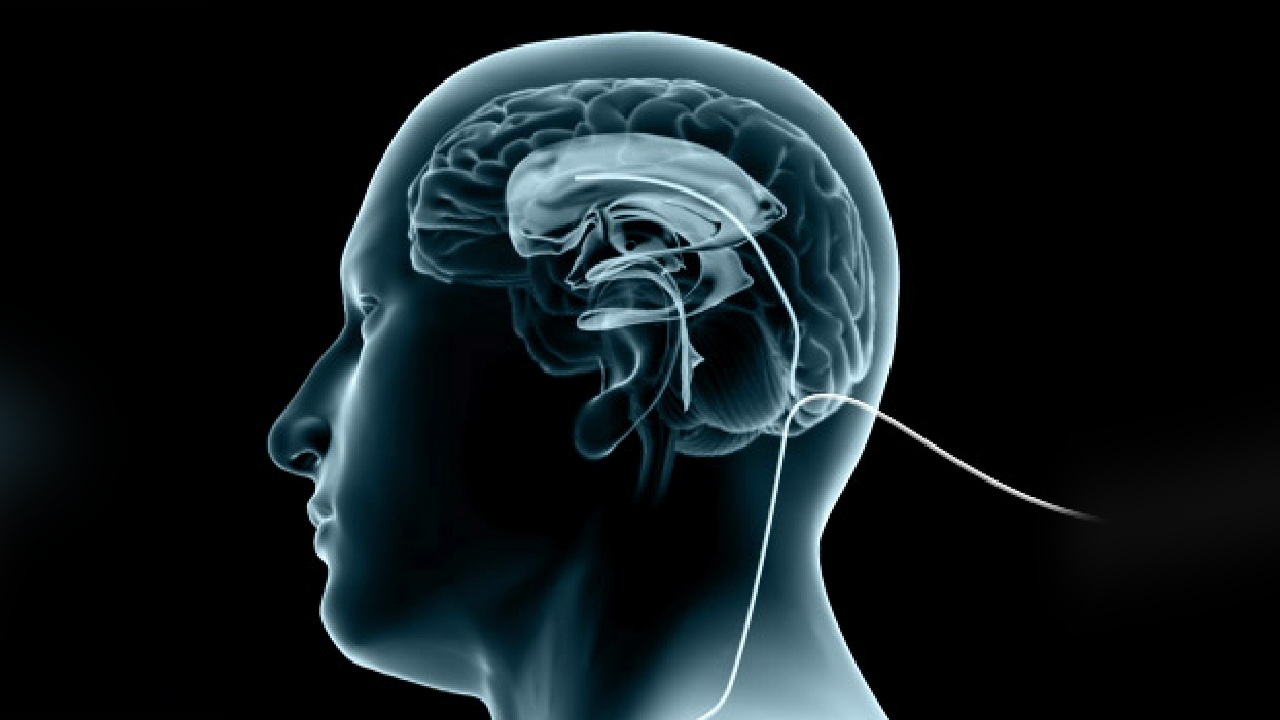
- Shunt placement: Hydrocephalus is most commonly treated with a shunt. When surgically implanted, a thin tube diverts excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the brain to the abdominal cavity or heart for absorption and elimination.
- Endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV): An ETV is a procedure used to treat obstructive hydrocephalus, especially when cerebral aqueduct blockage is present, by creating a hole in the third ventricle floor.
- Medications: Hydrocephalus symptoms include headaches, nausea, and seizures, which can be treated with medicines and diuretics to decrease CSF production and intracranial pressure.
- Regular monitoring and follow-up: Hydrocephalus patients require regular healthcare monitoring to assess symptoms, monitor shunt function, and make necessary treatment adjustments.
- Management of underlying causes: Hydrocephalus can be a secondary condition to an underlying condition like a tumour or infection, necessitating treatment for the underlying cause in addition to hydrocephalus treatment. Hydrocephalus treatments can manage symptoms and improve quality of life, but they may not cure the condition completely. In cases of progressive neurological conditions or structural abnormalities, it may not be possible to eliminate symptoms or restore normal brain function completely. Individuals with hydrocephalus should collaborate with a multidisciplinary healthcare team to develop a personalised treatment plan, with regular follow-up evaluations to monitor and adjust treatment.
The following precautions were taken to ensure a swift recovery from hydrocephalus in adults
- Follow medical advice:
Hydrocephalus patients should follow healthcare professionals’ treatment recommendations, including prescribed medications, regular appointments, and prompt medical attention for new symptoms, as per their healthcare provider’s plan.
- Monitor symptoms:
Monitoring and promptly reporting symptom changes to your healthcare provider can help identify potential complications or necessary treatment adjustments, ensuring a comprehensive and timely diagnosis.
- Shunt care:
- Following the neurosurgeon’s care instructions for hydrocephalus shunts is crucial, including avoiding activities that could damage the shunt, such as contact sports or sudden head movements.
- Avoid activities that may injure the shunt, such as contact sports, excessive lifting, or unexpected head blows.
- Be aware of symptoms of shunt malfunction or infection, such as headache, nausea, vomiting, changes in mental state, or evidence of infection near the shunt site (redness, swelling, drainage).
- Seek medical assistance right once if you notice any symptoms of shunt dysfunction or infection.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can enhance overall well-being and alleviate hydrocephalus symptoms.
- Consuming a balanced diet that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats is essential for overall health.
- Regular physical activity, as per your healthcare provider’s guidelines or restrictions, should be maintained as tolerated.
- Getting sufficient sleep and incorporating stress-reduction techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga can help manage stress effectively.
- Hydration: Maintaining healthy cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) levels requires adequate hydration throughout the day unless advised by a healthcare provider.
- Avoid head trauma: Prevent head injuries to ensure proper function of the shunt and prevent hydrocephalus symptoms.
- Attend rehabilitation and therapy: Participate in rehabilitation programmes such as physical therapy, occupational therapy, or speech therapy as directed by your healthcare physician. These programmes can assist in enhancing physical function, mobility, and cognitive capacities, leading to a quicker recovery.
Recovery from hydrocephalus is a gradual process, with individual outcomes varying. Supporting overall health and consulting with healthcare providers for personalised recommendations can improve recovery outcomes.
About Dr Vishakha
Dr. Vishakha Karpe, a highly skilled Senior Paediatric Neurosurgeon at Rainbow Children’s Hospital, Banjara Hills, and Hyder Nagar in Hyderabad, is one of India’s leading paediatric neurosurgeons with extensive experience in paediatric neurosurgery. With over nine years of dedicated practice, she is among the few in India working extensively in this field.
With extensive experience in pediatric neurosurgical conditions, she focuses on comprehensive care, including precise surgery and educating parents about the complete case management protocol. She is an efficient and passionate medical professional, pursuing ethical practice and ensuring patient care after surgery.
Proficiency of Dr Vishakha:
-
-
Hydrocephalus (increased fluid in the brain): The procedure involves an endoscopic third ventriculostomy and CSF diversion (VP shunt) to treat complex hydrocephalus.
- Craniosynostosis (abnormal head shape due to untimely cranial sutures fusion) surgeries: Helmet therapy is a technique that is used in both endoscopic and open surgery.
-
- Spinal dysraphisms(Spina Bifida)- (spinal abnormalities present by birth) – surgical repair
- Encepahaocles repair surgery.
-
- Vascular conditions and stroke surgeries: revascularization surgeries for moya moya disease.
- Pediatric brain and spine tumour surgeries.
-
- Pediatric brain and spine infection surgeries: Endoscopic and open surgeries for brain and spine infections.
- Pediatric traumatic brain and spinal injury.
- Antenatal counselling for congenital fatal neurosurgical conditions.
Dr Vishakha Patil specializes in craniosynostosis surgery, which is only done in a few centres in India. Dr Vishakha Patil, M.B.B.S, DNB (AIIMS) New Delhi, M.Ch (IPGMER SSKM) became a Member of “The Royal College of Surgeons, Edinburgh” (U.K.) a highly successful and best pediatric neurosurgeon in Hyderabad, Telangana with 13 years of experience, is among the topmost pediatric neurosurgeons in the Rainbow group of hospitals at Hyder Nagar and Banjara Hills.